Explain how to use the OSGi Service
Refer1
Refer2
Refer3
Refer4
1. Introduction
- OSGi Services are essentially Java objects that provide a specific functionality or interface, and other components,plugins can dynamically discover and use these services.
- Multiple plugins can provide a service implementation for the service interface. Plugins can access the service implementation via the service interface.
- E.g. When you want to create modular that can be added or removed at runtime, you can use the OSGi service.
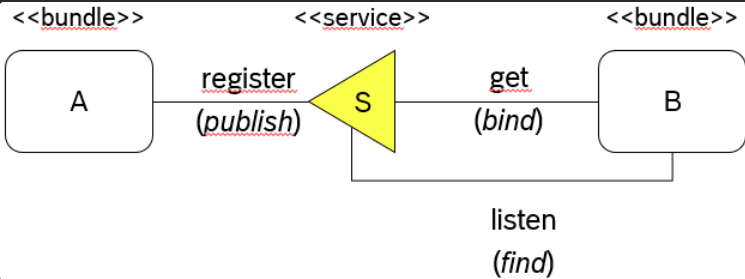
-
Bundle Aprove/publish a service implementationS. -
Bundle Bcan consume it by finding the service and binding to it when it is found. -
There can be multile
service implementation(Bundle A’, A’’’) published at the same time for the same typeS. -
Services in OSGi are dynamic and can come and go at runtime.
-
OSGi Service Registryis a controller. -
OSGIvsEquinox Extension Point:OSGiis many-to-many relationship (multiple bundles can provide <-> multiple bundles can consume).Equinox Extension Pointis one-to-many relationship (actually we can workaround accessing viaExtensionRegistry).OSGi Servicesare retried bytype-> safeEquinox Extension Pointaccess viaID
With OSGi Declarative Services it is not necessary to register or consume services programmatically. This needs to be done with plain OSGi services where a service is typically registered (publish) to the ServiceRegistry in an Activator and consumed (find-bind) via ServiceTracker (also mostly via Activator). Instead of this a Service Component is declared via Component Description when using declarative services. The Component Description is an XML file that is processed by a Service Component Runtime (SCR, e.g. Felix SCR) when a bundle is activated. It is responsible for managing the components and their life cycle. That means, if you want to use declarative services in your application, you need to ensure that a Service Component Runtime bundle is installed and activated in your environment.
1.1. Components
-
Service Component: A Java class that is declared via Component Description - not every component provides a service (e.g. inDoingSomethingService.java- @Component(service = IDoingSomethingService.class)) -
Component Description: The declaration of aService Component, contained in the XML file (OSGI-INF/myservice.xml) -
Component Properties: A set of properties, specific by theComponent Description -
Component Property Type: User define annotation type to define the Component Properties -
Component Configuration: -
Component Instance: -
e.g:
-
MANIFEST.MF
Service-Component: OSGI-INF/componentDescription.xml,
- Java:
@ComponentPropertyType
public @interface MyComponentProperties{
String value();
boolean isOk();
}
public interface IMyService{
void doSomething();
}
@Component(service = IMyService.class)
@MyComponentProperties(value = "1", isOke = true)
public class MyService implements IMyService{
@Override
void doSomething(){
// do something here
}
}
- XML automatically generate for OSGi Declare Service
1.2. Declaring a Component
- A component requires the following artifacts in the bundle:
- An XML document that contains the component description.
- The Service-Component manifest header which names the XML documents that contain the component descriptions.
- An implementation class that is specified in the component description.
1.2.1 Immediate Component
- An immediate component is activated as soon as its dependencies are satisfied.
/OSGI-INF/activator.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<scr:component name="example.activator"
xmlns:scr="http://www.osgi.org/xmlns/scr/v1.4.0">
<implementation class="com.acme.impl.Activator"/>
</scr:component>
- The manifest header
Service-Componentmust also be specified in the bundle manifest (MANIFEST.MF)
Service-Component: OSGI-INF/activator.xml
- Java class for this component
public class Activator {
protected
public Activator() {...}
@Activate
private void activate(BundleContext context) {...}
private void deactivate() {...}
}
The activate method is called when SCR activates the component configuration and the deactivate method is called when SCR deactivates the component configuration. If the activate method throws an Exception, then the component configuration is not activated and will be discarded.
1.2.2 Delayed Component
- Normally, it specifies a service
- If its configuration is satisfied, SRC must register the component in the service registry.
- When it is requested via
Service Caller, it will be activated. /OSGI-INF/handle.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<scr:component name="example.handler"
xmlns:scr="http://www.osgi.org/xmlns/scr/v1.4.0">
<implementation class="com.acme.impl.HandlerImpl"/>
<property name="event.topics">some/topic</property>
<service>
<provide interface="org.osgi.service.event.EventHandler"/>
</service>
</scr:component>
- Java class declare:
public class HandlerImpl implements EventHandler{
public void handleEvent(Event evt ) {
...
}
}
2. Using OSGi
- There are several ways of defining, providing and consuming service.
- Let’s start with create the API project to provide the external APIs for other components.
2.1. Create API project
2.2. Specific the API
- Create an interface for the service definition.
package com.test.internal;
/**
* Service for doing something
*
* @noimplement This interface is not intended to be implemented by clients.
* @noextend This interface is not intended to be extended by clients.
*/
public interface IDoingSomethingService {
public void doSomething();
}
- Create the service implementation that implements service interface.
@Component(service = { DoingSomethingService.class, IDoingSomethingService.class }, immediate = false)
public class DoingSomethingService implements IDoingSomethingService{
@Override
public void doSomething(){
syserr("DoingSomethingService did something");
}
}
- Testing: ServiceCaller
ServiceCaller.callOnce(MyClass.class, IDoingSomethingService.class, (myService) -> myService.doSomething());
3 DS Annotations
3.1. @Component
- It i to identify the class as a Service Component and is used to generate the Component Description.
- Default:
Its name is the full qualified class name It registers all of the class’s directly implemented interfaces as services The instance will be shared by all bundles It is enabled It is immediate if it has no services, otherwise it is delayed It has an optional configuration policy The configuration PID is the full qualified class name
- The defaults can be changed via annotation type elements:
service: The name(s) of the interface or class this component is registered under as a service. Needs to be a full qualified class name.immediate: Control whether a component configuration should be immediately activated after becoming satisfied or if the activation should be delayed. Needs to be false in case the factory attribute is set also, needs to be true if no service is provided.- …
3.2. @Activate, @Deactivate, @Modified
-
Used to specify methods that should be called when a life cycle event happens.
@Activate: The method that should be called on component activation.@Modified: The method that should be called if a configuration is updated using the ConfigurationAdmin.@Deactivate: The method that should be called on component deactivation.
-
e.g.
@Activate
private void activate() {
//do some initialization stuff
}
3.3. @Reference
-
Used to specify the dependency on other services.
-
When the annotation is applied to a method, the method is the bind method of the reference.
-
When the annotation is applied to a field, the field will contain the bound service(s) of the reference.
-
Field Injection
@Component
public class MyComponent {
@Reference
private MyService myService;
public void doSomething() {
myService.execute();
}
}
Khi MyService có trong OSGi Service Registry, nó sẽ tự động được inject vào myService.
Nếu không có MyService, myService sẽ là null.
- Method Injection
@Component
public class MyComponent {
private MyService myService;
@Reference
protected void bindMyService(MyService myService) {
this.myService = myService;
}
protected void unbindMyService(MyService myService) {
if (this.myService == myService) {
this.myService = null;
}
}
}
Phương thức bind (bindMyService): Được gọi khi MyService có sẵn trong Service Registry.
Phương thức unbind (unbindMyService): Được gọi khi service bị gỡ khỏi Registry.
❗ Đây là cách tốt để xử lý service lifecycle (khi service bị remove).
0.
.settings/org.eclipse.pde.ds.annotations.prefs
dsVersion=V1_4 # Sử dụng phiên bản Declarative Services 1.4 (OSGi R7)
eclipse.preferences.version=1 # Phiên bản định dạng file .prefs (mặc định của Eclipse)
enabled=true # Bật xử lý annotation DS (bắt buộc để sinh file XML)
generateBundleActivationPolicyLazy=true # Tự động thêm “Bundle-ActivationPolicy: lazy” vào MANIFEST.MF
path=OSGI-INF # Thư mục sẽ chứa file XML được sinh (mặc định là OSGI-INF)
validationErrorLevel=error # Nếu annotation sai thì hiện lỗi trong Eclipse (mức: error)
validationErrorLevel.missingImplicitUnbindMethod=error # Báo lỗi nếu thiếu unbind method khi dùng @Reference