Java is a programming language created by James Gosling from Sun Microsystems (Sun) in 1991. Java allows to write a program and run it on multiple operating systems.
References:
Java Platform Standard Edition 8 Documentation
Introduction to Java programming - Tutorial
1. Introduction to Java
Oracle has two products implement Java SE:
- JDK (Java SE Development Kit): is a superset of JRE.
- JRE (Java SE Runtime Environment): provides the libraries, the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) and other components.
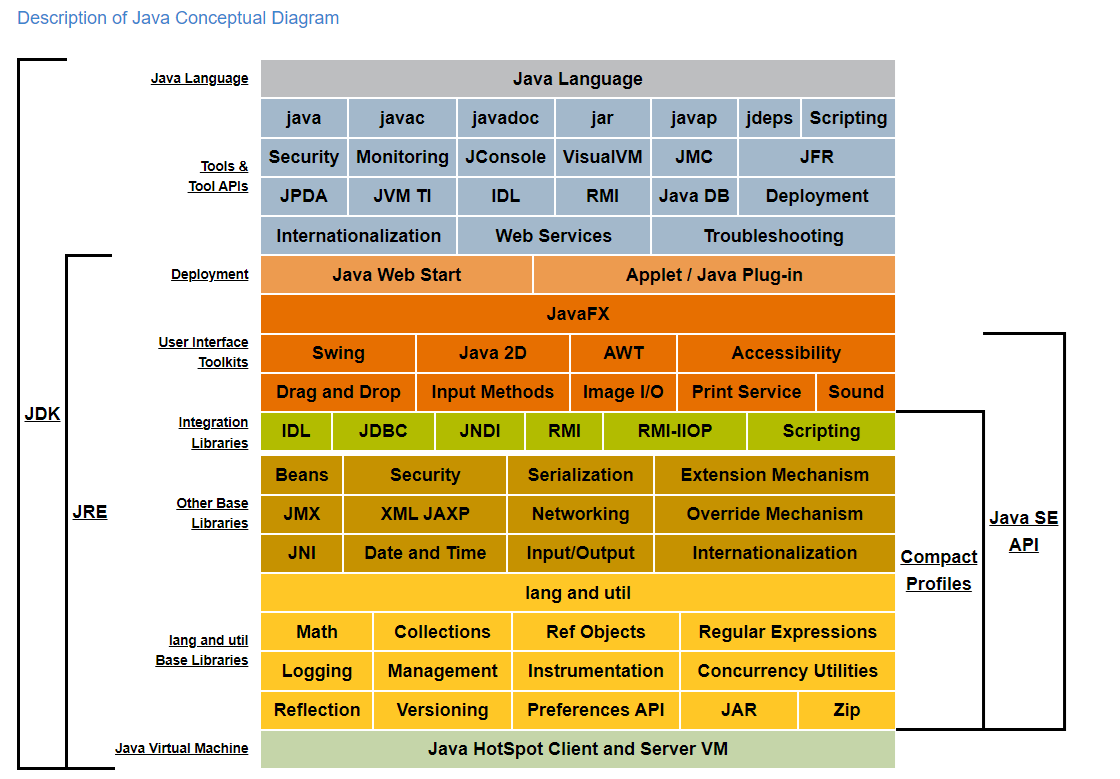
1.1. Development Process with Java
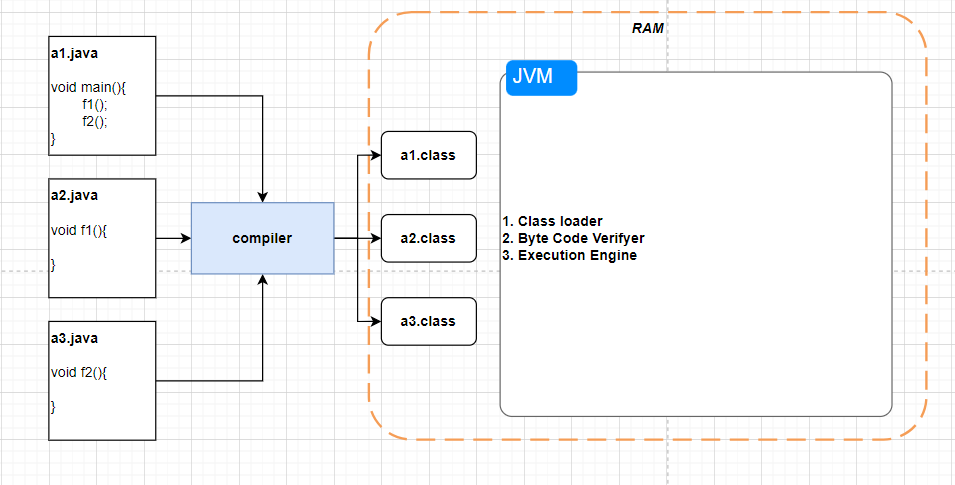
- Source code is first written in
.javafile. - Those source files are then compiled into
.classfiles by the Java compiler(javac). - A
.classfile containsbytecodes(the machine language of the Java VM). - The
.classfile will be run by Java tool as an instance of the Java VM. - The Java virtual machine (JVM) is a software implementation of a computer that executes programs like a real machine.
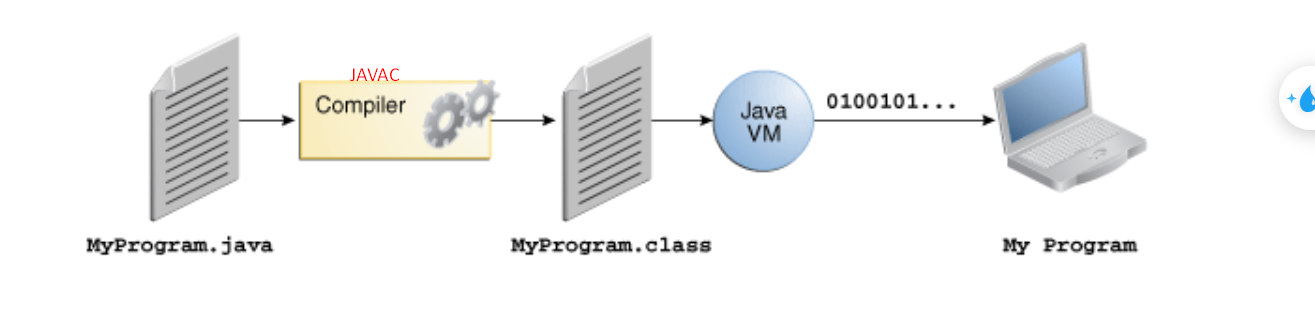
Because the Java VM is available on many different OS, the same .class files are capable of running on many OS too.
1.2. Comparison of the C and Java Compilation & Linking Processes
1.3. Garbage collector
- The Java runtime automatically frees the memory which is not referred to by other objects.
- The Java garbage collector checks all object references and finds the objects which can be automatically released.
1.4. Classpath
- The
classpathdefines where the Java compiler and Java runtime look for.classfiles to load. - If we want to use an external Java library we have to add this library to our
classpath
To use the classpath, type the following command. Replace “mydirectory” with the directory which contains the test directory(.class file etc).
java -classpath "mydirectory" HelloWorld
2. Installation
- To run Java programs, we must have
Java Runtime Environment (JRE)
>java --version
java 21.0.3 2024-04-16 LTS
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 21.0.3+7-LTS-152)
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 21.0.3+7-LTS-152, mixed mode, sharing)
- Write a source file named
HelloWorld.java
// a small Java program in HelloWord.java
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}
- Compile a Java source file in to a class file
javac HelloWorld.java - Start the Java program and we should see “Hello Word” on the command line:
C:\Users\phong.nguyen-van\Desktop>java HelloWorld
Hello World
3. Trail: Learning the Java Language
This trail covers the fundamentals of programming in the Java programming language.
- Object-Oriented Programming Concepts teaches you the core concepts behind object-oriented programming: objects, messages, classes, and inheritance. This lesson ends by showing you how these concepts translate into code. Feel free to skip this lesson if you are already familiar with object-oriented programming.
- Language Basics describes the traditional features of the language, including variables, arrays, data types, operators, and control flow.
- Classes and Objects describes how to write the classes from which objects are created, and how to create and use the objects.
- Annotations are a form of metadata and provide information for the compiler. This lesson describes where and how to use annotations in a program effectively.
- Interfaces and Inheritance describes interfaces—what they are, why you would want to write one, and how to write one. This section also describes the way in which you can derive one class from another. That is, how a subclass can inherit fields and methods from a superclass. You will learn that all classes are derived from the Object class, and how to modify the methods that a subclass inherits from superclasses.
- Numbers and Strings This lesson describes how to use Number and String objects The lesson also shows you how to format data for output.
- Generics are a powerful feature of the Java programming language. They improve the type safety of your code, making more of your bugs detectable at compile time.
- Packages are a feature of the Java programming language that help you to organize and structure your classes and their relationships to one another.
- Others:
4. Study
4.1. Pattern/Matcher - java.until.regex
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
// Example 1: check matching
public class REGEX {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String regex = "com\\.something.*"; //$NON-NLS-1$
String input = "com.something.test";
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(input);
if(matcher.matches()) {
System.err.println("Match !!!");
}else {
System.err.println("Do Not Match !!!");
}
}
}
// Example 2: Find and replace
Map<String, String> replacements = new HashMap<String, String>() {{
put("${env1}", "1");
put("${env2}", "2");
put("${env3}", "3");
}};
String line ="${env1}sojods${env2}${env3}";
String rx = "(\\$\\{[^}]+\\})";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); //use StringBuffer before Java 9
// Note: StringBuffer is sync but slower than StringBuilder
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(rx);
Matcher m = p.matcher(line);
while (m.find())
{
// Avoids throwing a NullPointerException in the case that you
// Don't have a replacement defined in the map for the match
String repString = replacements.get(m.group(1));
if (repString != null)
m.appendReplacement(sb, repString);
}
m.appendTail(sb);
System.out.println(sb.toString());
4.2. URL - URI
-
URI: Uniform Resource Identifier: the complete identification of any resources. e.g.urn:isbn:1234567890 -
URL: Uniform Resource Locator: a subset of URI that, in addition to identifying where a resource is available. And let we know the mechanism to access it. e.g."http://somehost:80/path?thequery" -
Every
URLis aURI, but the opposite is not true. -
URI syntax:
scheme:[//authority][/path][?query][#fragment]scheme: protocol to access the resourceauthority: optional part, include user,host, port,…path: identify a resourcequery: also identify a resource, for URLs, this is the query stringfragment: optional part, specific part of the resource
-
URI have ftp, http, https, file wil be a URL.
The easiest way to see the difference between URL and URI is to remember that: URI = identifier (the broad concept — anything that uniquely names or locates a resource) URL = locator (a URI that tells you where and how to get it) URI ├── URL → has location + access method └── URN → name only, no access method
URI.create("file:///Users/joe/FileTest.java"