This is where I study English grammar on my own every day. It’s a place where I not only improve my language skills but also discover new grammar rules. Step by step, I am working to become more confident in writing and communicating in English. The journey isn’t easy, but I believe that with patience and effort, I will continue to make progress.
1. Tenses
Tenses indicate the time of an action or state of being expressed by a verb.
1.1. Present
1.1.1. Present Continuous ( I am doing)
-
Usage: Started doing it and I haven’t finished. In the middle of doing it.

-
Structure:
- be:
am/is/are being - P:
am/is/are V-ing - N:
am/is/are not V-ing - Q:
am/is/are S V-ing
- be:
-
Time expressions: around now -
at the moment/ currently/ now/ today/ this week/ this year/ .. -
Examples:
He's being so selfish.// behaving selfishly nowI'm trying to work.I'm not working at the momentAre you working today?
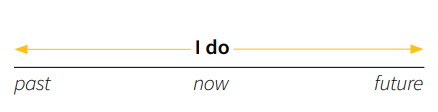
1.1.2. Present simple ( I do)
-
Usage: Express habitual actions, general truths, and states of being.
-
Structure:
- be:
am/is/are - P:
V/Vs_es - N:
do/does not V - Q:
do/does S V
- be:
-
Time expressions:
always/ usually/ often/ sometimes/ rarely/ never/ every day-week-month-year/ on Mondays/ at 5PM/ .. -
Examples:
He's selfish// He is selfish generallyI often work in the morning.He doesn't do that.Do you understand ?
-
see/hear/smell/taste
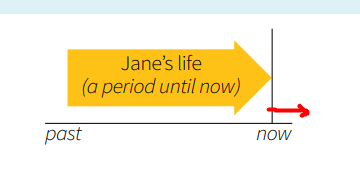
1.1.3. Present perfect ( I have done)
-
Usage: Describe actions that occurred at an unspecified time in the past, actions that have relevance to the present, or experiences that have happened over a period of time.
-
Structure:
- be:
have/ has been - P:
have/has Vpp - N:
have/has not Vpp - Q:
have/has S Vpp
- be:
-
Time expressions:
just: a short time agoalready: sooner than expectedyet: until nowsince: specific timefor: durationever:neverin the last few day:so far:this morning,.recently
-
Examples:
We've never had a carI haven't seen Tom this morning. Have you ?Have you had a holiday this year ?They have read that book// they read book at some unspecific time in the past and is relevant to the present moment.
-
How long have you been there ? -> I’ve been there for a long time.
1.1.4. Present perfect continuos( I have been doing)
- Usage: Describe actions that started in the past and continue into the present or have recently stopped, emphasizing the duration of the action.
She has been working here since 2020. (This emphasizes that her work started in 2020 and continues to the present.)
1.2. Past
1.2.1. Past Simple ( I did)
-
Usage: Started and finished in the past. Emphasizing that the action is complete and has no connection to the present.

-
Structure:
- be:
was/ware - P:
V-ed - N:
did not V - Q:
did S V
- be:
-
Time expressions:
yesterday/ last week-month-year/ in 2010, two days ago, on Monday (past), .. -
Examples:
I was ill.I visited to school last weekend.He didn't go to the party last night.Did you see that movie?
1.2.2. Past Continuous ( I was doing)
-
Usage: Describe actions that were ongoing at a specific time in the past. It indicates that the action started before this time and was still in progress at that time.
-
Structure:
- be:
was/ware being - P:
V-ed - N:
did not V - Q:
did S V
- be:
-
Time expressions: Before a specific time in the past. (Matt phoned, at 10 o’clock last night, ..While.., ..when..,)
-
Examples:
He was being cautious.// he was acting in a careful at that time.Matt phoned while we were having dinner.I waved to Helen, but she wasn't looking.Were they playing football at 10 o'clock last night.
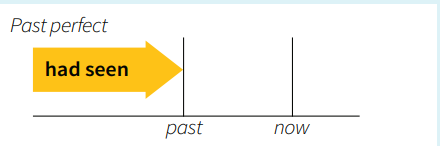
1.2.3. Past Perfect ( I had done)
-
Usage: Describe an action that was completed before another action or time in the past. It emphasizes the sequence of events.
-
Structure:
- P:
had Vpp - N:
had not Vpp - Q:
had S Vpp
- P:
-
Time expressions:
before/ after/ when/ by the time/ already .. -
Examples:
I had finished my homework before the party started.They hadn't seem that movie until last week// they had not watched the movie up to that point in time.Had you ever visited Paris before your trip last year?
1.2.4. Past Perfect continuous( I had been doing)
- Usage: Emphasizes the duration
Had you been waiting long before the bus arrived?// This asks about the duration of the waiting period before the bus arrived.
1.2.5. Used to
-
Structure:
used to V: refers to past habits or state that are no longer true.be used to Ving/N: indicates familiarity or comfort with a situation in the present.
-
Examples:
I used to play the game, which was named 3Q, when I was younger.I am not used to cold weather.// The cold weather is unfamiliar for me
1.3. Future
1.3.1. Present tenses for the future (I do/ I am doing)
-
Usage:
- I do: Often used for fixed events or timetables (e.g., trains, schedules, public events).
- I am doing: Used for personal plans or arrangements, typically those that are already decided or prepared.
-
Examples:
The train leaves at 6 PM.// fixed scheduleWe are having a meeting next week// the plan decided
1.3.2. I’m going to do

- Usage: I’ve decided to do it. Maybe I’ve arranged to do it, maybe not.Often based on current evidence or situations.
- Examples:
I'm going to clean the room// I’ve decided to clean them, but I haven’t arranged this.It's going to rain// see the clouds and make state
was going to: planed but did not happen: I was going to call you, but I forgot
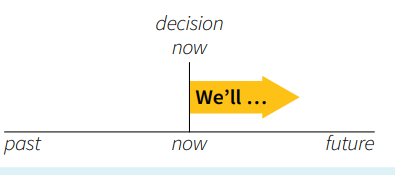
1.3.3. Future simple ( I will)
-
Usage: Express actions that will happen at a later time. It often conveys predictions, spontaneous decisions, promises, and facts about the future.
-
Structure:
- P:
will V - N:
will not/ won't V - Q:
will S V
- P:
-
Time expressions:
tomorrow/ next week-month-year/ in few days/ soon/ later -
Often use with:
- I’ll probably be home late tonight.
- I’m sure you will …
- I think I will do …
- I wonder what will happen.
-
Examples:
I had finished my homework before the party started.They hadn't seem that movie until last week// they had not watched the movie up to that point in time.Had you ever visited Paris before your trip last year?
-
I will do st when I do something/ when something happens.
1.3.4. Future continue (I will be doing)
-
Usage: Describe actions that will be in progress at a specific point in the future. It emphasizes the ongoing nature of the action during that future time.

-
Structure:
- P:
will be V-ing - N:
will not/ won't be V-ing - Q:
will S be V-ing
- P:
-
Time expressions: specific point in the future -
at this time/ ... -
Examples:
I will be working on the project tomorrow afternoon
1.3.5. Future perfect (I will have done)
-
Usage: describe actions that will be completed before a specific point in the future. It emphasizes the completion of the action relative to that future time.
-
Structure:
- P:
will have Vpp - N:
will not/ won't have Vpp - Q:
will S have Vpp
- P:
-
Time expressions: by + specific point in the future -
by to morrow/ by the time/ by next week-month-year/ before.. -
Examples:
-
By this time next week, I will have done my task. -
Will you have been there by noon ?
1.3.6. Future perfect continuous (I will have been doing)
-
Usage: describe actions that will have been in progress for a duration of time up until a specific point in the future. It emphasizes the ongoing nature of the action and its duration before that future moment.
-
Structure:
- P:
will have been V-ing - N:
will not/ won't have been V-ing - Q:
will S have been V-ing
- P:
-
Time expressions:
until now/ since last week/ for two years/ by the end of this month/ by ...for -
Examples:
-
By the end of this month, I will have been working at the company for five years. -
Will you have been living here for a decade by next year
2. Type of words
This section categorizes words based on their function in a sentences(refer).
2.1. Nouns, pronouns and determiners
2.2. Verbs
2.3.2. Modal verbs
A. CAN - COULD - BE ABLE TO: Express ability or permission.
can: say that something is possible or allowed or somebody has the ability to do something.
We can see the lake from our hotel.
could say that somebody had the ability to so something, or was allowed to do something.
- E.g.
When I was younger, I could run fast. could have happened = it was possible, but did not happen.
be able to: like can but is less usual. Can has only 2 forms: present(can) and past (could), so it’s necessary to use be able to sometime.
is able to = can | was able to/managed to = could
I will be able to attend the meeting
B. MAY - MIGHT: Say something is possible
C. HAVE TO - MUST:
D. SHOULD :
E. REQUESTS - OFFERS - PERMISSION - INVITATION
- Request:
asking people to do things- Can/ Could you wait a moment, please ?
- Do you think you could take me to the airport ?
asking for things- Can/ Could I/we have the menu, please ?
- May I have these postcards, please ?
asking todo things- May I ask you a question ? (formal)
- Can/Could I use your phone charge, please ?
- Do you think I could borrow your bike ?
- Do you mind if I use your phone charge ?
- Is it all right if I sit here ?
- Offering:
to offer to do something- Can I help you ?
- Would you like some coffee ? Would you like to eat with us tonight ?
- I’d like/ I would like to try on this jacket, please.
2.3.3. Verb patterns -ing and to …
2.3.4. Phrasal verbs
2.3.5. Others
2.3. Adjectives and adverbs
2.4. Conjunctions and prepositions
3. Types of sentences
3.1. Questions
3.1.1 Yes or No
- Usage: To respond to yes/no question.
- Structure:
AV + S + V ... ? - Yes/No, S + AV (not) ... - Examples:
Are you going to work today ?- ->
Yes, I'm going to work today.
- ->
3.1.2 Information - Subject
- Usage: Used to inquire about the subject of an action.
- Structure:
Who/What + V ... ?
- Examples:
Who opened the door ?- ->
William opened the door.
- ->
3.1.3 Information - Object
- Usage: Used to ask about the object or recipient of an action.
- Structure:
Whom/What + AV + S + V ... ?
- Examples:
What did you buy at the store ?- ->
I bought a book.
- ->
3.1.4 Information - Additional
- Usage: Used to ask for details like place, time, reason, or manner of an action.
- Structure:
When/Where/Why/How + AV + S + V ... ?
- Examples:
How did you get to work today ?- ->
I took the bus.
- ->
3.1.5 Embedded question
- Usage: Used for indirect or polite questions. Follow statement order without inverting the subject and auxiliary verb.
- Structure:
Main Clause + Question Word + Subject + Verb (no inversion). - Examples:
Do you know how she solved the problem ?- ->
She figured it out by asking for help.
- ->
Could you explain how this machine work ?- ->
It operates by pressing the green start button.
- ->
3.1.6 Tag
- Usage: Used to confirm or check the accuracy of a statement.
- Structure:
Main clause , tag ?
- Examples:
She should stay in bed, shouldn't she ?No one is here, are they ?This is your book, isn't it ?- …
3.2. If
3.2.1 Unless
- Usages:
Unless = If ... not - Examples:
If we don't start at once, we will be late.= Unless we start at once, we will be late.
3.2.2 If I do
- Usage: Express a condition that is possible or likely to happen in the present or future.
- Structure:
If present simple , future simple. - Examples:
If I have enough money, I will buy a new car.Should I have enough money, I will buy a new car.
3.2.3 If I did
- Usage: Express a hypothetical condition that is not true or unlikely in the present or future.
- Structure:
If past simple , S would/could/should V - Examples:
If **I were** the president, I would build more hospitals.Were I the president, I would build more hospitals.
3.2.4 If I had done
- Usage: Express a hypothetical condition that is not true or unlikely in the past.
- Structure:
If past perfect , S would/could/should have Vpp - Examples:
If we had found him early, we could have saved his life.Had we found him early, we could saved his life.
3.2.5 If past perfect, S would + V.
- Usage: Expresses a condition that was not true in the past and its hypothetical result in the present. If that condition had occurred in the past, the result would be different in the present.
- Structure:
If past perfect, S would V - Examples:
If I had been born in town, I would like life there now
3.3. Wish / If only
- Usage: Express a desire or longing for something that is not currently or a hypothetical situation. It conveys a sense of regret or an unrealized aspiration.
- Can replace “I wish” with “If only” to add emphasis to your regret or desire in a sentence. I wish you could join us for the party = If only you could join us for the party.
- When we want to express a present wish with emphasis on an ongoing or continuous action, you can use the continuous tense. If only my computer were working now.
3.3.1. For present unreal situations
- Structure:
I wish S V-ed - Examples:
I wish I were taller
3.3.2. For past unreal situations
- Structure:
I wish S had Vpp - Examples:
I wish I had studied harder.
3.3.3. For future possibilities
- Structure:
I wish S could V - Examples:
I wish I could travel more.
3.3.4. To express good wishes for others
- Structure:
I wish you could VI wish you NMay you V
- Examples:
I wish you could join us for the party.I wish you all the best->I wish all the best for youMay you have a prosperous year
3.3.5. To do something/ Some body to do something
- Structure:
I wish to VI wish you to V
- Examples:
I wish to drink a cup of coffee.I wish him can know how I feel now.
3.3. Passive
3.3.1 Formal
- Usage: Passive is used to emphasize the action itself or the receive of action, rather than it does.
- Structure:
be + the past participle of the verb
| Active | Passive | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| do | is done | Someone cleans this room everyday - This room is cleaned every day |
| is/are doing | is/are being done | |
| did | was done | |
| was/were doing | was/ware being done | |
| has/have done | has/have been done | |
| had done | had been done | |
| will do | will be done | |
| will have done | will have been done | |
| is/are going to | is/are going to be done | |
| can/could/ might/must/ have to do | can/could/might/must/ have to be done |
3.3.2 Passive with reporting verbs - It is said/ People say
- Usage: Used to report general beliefs, expectations, or statements in a formal or indirect way.
- Structure:
It is said (believed / thought / expected) that …People say that …
- Examples:
It is said that he is a genius.People say that he is a genius.
3.3.3 Is to be done
- Usage: Expresses a requirement, instruction, or intention in a formal way.
- Structure:
S be to be Vpp - Examples:
This report is to be completed by Friday.
3.3.4 Have something done
- Usage: Used to indicate a service or action that someone arranges to be done by another person.
- Structure:
S have O Vpp - Examples:
I had my car washed// I arranged for someone to wash my car
get something done: less formal -> He got his house painted last sumer.
3.4. Reported speech
- Usage: Reported speech is used to tell someone what another person said without quoting their exact worlds.
- Structure:
John said/told me/ asked me (that) subject verb_in_shifted_tensetell/ask somebody tosomebody said (not) to do something
- Examples:
"I am tired", she said"- ->
She said that she was tired
- ->
"Please help me", he asked- ->
He asked me to help him
- ->
"Do you like pizza ?", Ly asked- ->
Ly asked if(whether) I liked pizza
- ->
3.5. Relative clauses
- Usage: Relative clauses are a type of subordinate clause that gives more information about a noun.
3.5.1. Type of Relative clauses
- Defining Relative Clauses
The man who lives next door is a doctor.
- Non-Defining Relative Clauses
My brother, who lives in London, is coming to visit.
3.5.2. Relative Pronouns
- Who:
I told you about the woman who lives next door.
- Which:
Do you see the cat which is lying on the roof ?.
- Whose:
Do you know the boy whose mother is a nurse.
- That:
I don't like the table that stands in the kitchen.
3.5.3. Relative Adverbs
- When (in/at/on which):
I remember the day when we first met.
- Where (in/at/on which):
I remember the place where we met him.
- Why (for which):
The reason why we did not play football yesterday is so bad.
3.5.4. Reduced clauses
The man who is standing there is handsome-
The man standing there is handsome.
-
The book which is written by Mr.A is interesting.-
The book written by Mr.A is interesting.
-
He is the only man who can solve this problem.-
He is the only man to solve this problem.
-
The breaker that is on the counter contains a solution-
The breaker on the counter contains a solution
-
The woman, who is very clever and beautiful is my aunt.-
The woman, clear and beautiful is my aunt.
-
3.6. Noun clauses
3.6.1. Subject Clause
- Usage: Noun clauses that act as the subject of a sentence.
- Structure:
Where/When/Why/What/That S V - Examples:
When he leaves is up to me.
3.6.2. Object of Verb
- Usage: Noun clauses that act as the object of the verb.
- Structure:
S V w.../that S V - Examples:
They think that they are wrong.
3.6.3. Object of Preposition
- Usage: as the object of preposition
- Structure:
adjective + preposition + w.../that SV - Examples:
He is interested in how we could do that.
3.6.4. Subject Complement
- Usage: as complements to the subject.
- Structure:
S be + w.../that S V. - Examples:
The problem is where you are now.
3.7. Adverbial Clauses
3.7.1. Time Clauses
- Usage: Indicates the time when the action in the main clause occurs.
- Structure:
When + subject + verb
While + subject + verb
Before + subject + verb
After + subject + verb
Since + present perfect
As + subject + verb
Till/Until + subject + verb
As soon as + subject + verb
Just as + subject + verb
Whenever + subject + verb
- Examples:
When he comes, I will tell him the news.I am reading a book while they are playing soccer.He went out after he had finished the housework.I haven’t met them since they left.I saw her as I was shopping in the supermarket.I’ll wait until he comes back.As soon as Mary knew the truth, she called me.Just as the girl entered the room, everyone looked at me.I’ll come whenever you need me.
3.7.2. Place Clauses
- Usage: Indicates the place where an action occurs.
- Structure:
Where/ Wherever S V - Examples:
You can find me where you live, near the park.
3.7.3. Cause Clauses
- Usage: Explains the reason for an action.
- Structure:
Because/ Since/ As/ Seeing that S V - Examples:
Seeing that they were late, they missed the first part of the movie.
3.7.4. Purpose Clauses
- Usage: Indicates the purpose of an action.
- Structure:
So that/ In order that S V - Examples:
Many students write to the president in order that Black people may achieve equality.
3.7.5. Contrast Clauses
- Usage: Expresses contrast or opposition between two ideas or actions.
- Structure:
Although/ Though/ Even though S VBut/ Yet S VWhile/ Whereas S V
- Examples:
Though she has a lot of things to do, she still spends time playing with her children.He loves her, but he can’t marry her.Whereas she is short, her husband is tall.
3.8. Comparative
- Usage: Used to compare two things, showing they are similar (or not) in some way.
3.8.1. Equal - using “Adj/Adv”
- Structure:
S + V + as adj/adv as + noun/ pronoun/ SV. - Examples:
This book is as interesting as yours.
3.8.2. Equal - using “the same Noun”
- Structure:
S + V + the same (N) as + noun/pronoun/ SV. - Examples:
My house is the same height as his.
3.8.3. Equal - using Quantities
- Structure:
S + V + as many/much/little/few N as + noun/pronoun/ SV. - Examples:
She has as many book as I do.
3.8.4. Equal - Negation
- Use “not as” or “not so” for negative comparisons.
The teacher is not the same as ours
3.8.5. Less/More - using “Adj/Adv”
- Structure:
S + V + (intensifier) + adj/adv (er) than + noun/pronoun/SVS + V + more/less adj/adv than + noun/pronoun/SV
- Intensifiers: far, even, much, still, a lot
- Examples:
Today is hotter than yesterday.My lover is more beautiful than me.
3.8.6. Less/More - using “Noun”
- Structure:
S + V + more/fewer/less Noun than + noun/pronoun/SV
- Examples:
She has fewer books than me.
3.8.7. Multiplicative
- Structure:
S + V + (twice/three times/…) as much/many/noun as + noun/pronoun
- Examples:
This car is three times as expensive as that one.
3.8.8. Correlative
- Structure:
The comparative + S + V, the comparative + S + VThe more + S + V, the comparative + S + V
- Examples:
The sooner you take it, the better you will feel.The more you study, the smarter you will become.
3.8.9. Superlative
- Structure:
S + V + the adj/adv (est) + noun/SVS + V + the most/least adj/adv + noun/SVOne of the superlative + plural noun + S + V
- Examples:
One of the greatest clubs in the world is Barcelona.One of the greatest player of all time is Leo Messi.